In an increasingly industrialized world where gases are utilized in various industries, from manufacturing and healthcare to energy production, the importance of gas detection cannot be overstated. Gas leaks can lead to catastrophic events such as fires, explosions, and health hazards. To prevent such incidents and ensure safety, it's essential to understand the basics of gas detectors.
What is a Gas Detector?
A gas detector is a critical safety device used to identify and monitor the presence of specific gases in the surrounding environment. These gases can include combustible, toxic, or asphyxiant gases like Carbon Monoxide (CO), Methane (CH4), Hydrogen Sulfide (H2S), and more. The primary purpose of gas detectors and monitors is to detect the presence of hazardous or potentially toxic gases, as well as monitor gas levels to mitigate potential risks and safeguard human health and the environment.
Role of Gas Monitors
Gas detectors are devices designed to identify and monitor the presence of hazardous gases in the environment. These gases can include flammable, toxic, or asphyxiant gases like Carbon Monoxide (CO), Methane (CH4), Hydrogen Sulfide (H2S), and many others. The primary functions of gas monitors are as follows:
- Protection of Lives: Gas detectors serve as early warning systems, alerting individuals to the presence of dangerous gases before they reach hazardous levels. This early detection provides people with the opportunity to evacuate or take necessary safety precautions, potentially saving lives.
- Ensuring Workplace Safety: In industrial environments where workers may be exposed to hazardous gases, gas monitors are essential for ensuring occupational safety. These devices are often worn by workers and trigger alarms if gas concentrations become dangerous.
- Preventing Environmental Disasters: Gas detectors are used to monitor and detect gas leaks in facilities such as chemical plants and gas storage facilities. By identifying leaks early, environmental disasters can be prevented, protecting ecosystems.
- Maintaining Process Control: In manufacturing industries, gas detectors are integrated into control systems to monitor gas levels during various processes. They enable automated shut-offs or adjustments to maintain safe operating conditions and product quality.
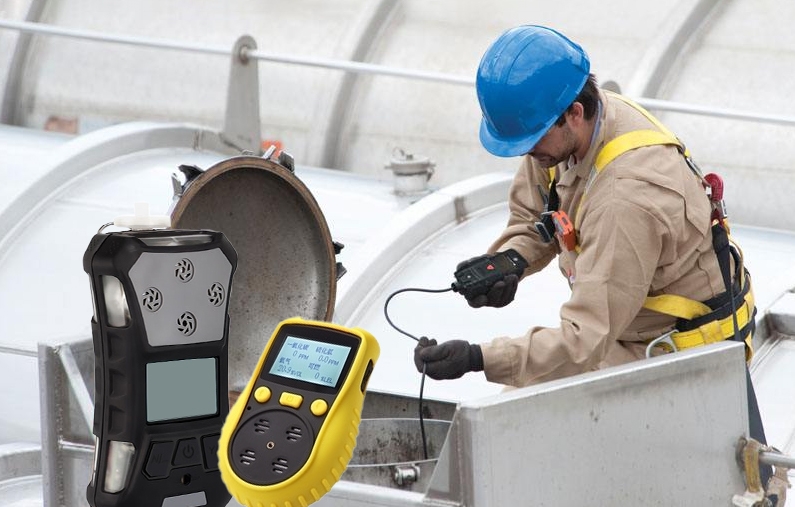

Gas Detectors Types
There are several types of GasDog gas detectors. These types include multi-gas detectors, single-gas detectors, fixed gas detectors, and portable gas detectors.
Single Gas Detector
- A single gas detector is a compact and specialized device designed to monitor and detect the presence of a single specific gas or vapor in the environment. These detectors are commonly used in workplaces where there is a known risk of exposure to a particular gas, such as Carbon Monoxide (CO), Hydrogen Sulfide (H2S), or Oxygen (O2).
- Single gas monitors are often worn by individuals as personal protective equipment (PPE) to provide continuous monitoring of their immediate surroundings. They are equipped with sensors or detectors that are selective to the target gas, and when the gas concentration reaches a dangerous level, the detector typically triggers an audible and visual alarm to alert the user.
Multi-Gas Detector
- A multi-gas detector, as the name suggests, is a more versatile device that can simultaneously monitor and detect the presence of multiple gases or vapors in the air. These detectors are commonly used in environments where workers may encounter various gases, providing comprehensive safety monitoring. Gas Dog multi-gas detectors are essential in industries like oil and gas, confined space entry, and chemical manufacturing.
- They feature multiple sensors, each designed to detect a specific gas, and can display real-time readings for each gas on the device's screen. In addition to alarms for individual gases, they often have alarms for the overall gas concentration or exposure.
Fixed Gas Detector
- A fixed gas detector is a stationary device installed in a specific location to continuously monitor the presence of gases in the surrounding environment. These detectors are commonly used in industrial settings, including factories, chemical plants, and refineries, where gas leaks can be hazardous and require immediate response.
- Fixed gas monitors are connected to a central control system and are typically placed in areas prone to gas leaks or in confined spaces. They can be set up to trigger alarms, ventilation systems, or shut-off valves if gas concentrations exceed preset safety thresholds.
- Fixed gas detectors often have a higher level of sensitivity and accuracy compared to portable detectors and are crucial for ensuring workplace safety.
Portable Gas Detector
- A portable gas detector is a handheld and battery-operated device designed for mobility and flexibility in gas detection tasks. These detectors are used by field workers, emergency responders, and maintenance personnel to assess gas concentrations in different locations.
- Portable gas detectors are typically lightweight and easy to carry, making them suitable for confined spaces or leak detection during inspections.
- They are available in both single-gas and multi-gas configurations, depending on the specific application. Portable gas detectors and monitors often come with features like data logging, built-in pumps for sample collection, and rugged construction to withstand harsh environments.
In summary, gas detectors come in various types to suit different applications. Single gas monitors are specialized for monitoring one gas, while multi-gas detectors provide comprehensive monitoring for multiple gases. Fixed gas detectors offer continuous monitoring in specific locations, and portable gas detectors provide flexibility and mobility for various gas detection tasks. The choice of gas detector depends on the specific industry, application, and safety requirements.
Types of Sensors
Gas detectors work using various sensing technologies to detect and monitor the presence of specific gases in the surrounding environment. The functioning of a gas monitor depends on the type of technology it employs, but the fundamental principle is to measure changes in the concentration of the target gas. Here are some common gas detection technologies and how they work:
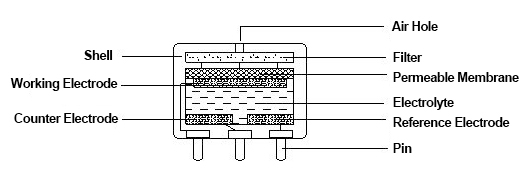
1. Electrochemical Sensors
- Principle: Electrochemical sensors detect gases through electrochemical reactions. When the target gas interacts with the sensor's electrode and electrolyte solution, it generates an electrical current or voltage that is directly proportional to the gas concentration.
- Applications: Electrochemical sensors are widely used for detecting toxic gases. For example, they are used for Carbon Monoxide (CO) detection in residential and industrial settings, Hydrogen Sulfide (H2S) monitoring in petrochemical industries, and Oxygen (O2) measurement in confined spaces.
- Advantages: High sensitivity, specificity, and accuracy. They can measure low gas concentrations and have fast response times.
- Limitations: Require periodic calibration and have a finite lifespan. Sensitivity can be affected by temperature and humidity.
2. Semiconductor Sensors
- Principle: Semiconductor sensors operate based on the change in electrical conductivity of a semiconductor material when exposed to specific gases. The interaction between the gas and the semiconductor results in a change in resistance or voltage.
- Applications: Semiconductor sensors are commonly used in portable gas detectors for gases like Hydrogen (H2), Methane (CH4), and volatile organic compounds (VOCs).
- Advantages: Cost-effective, fast response times, and suitable for portable devices. They can detect low gas concentrations.
- Limitations: Lack of specificity and may require frequent recalibration. Cross-sensitivity to other gases is possible.
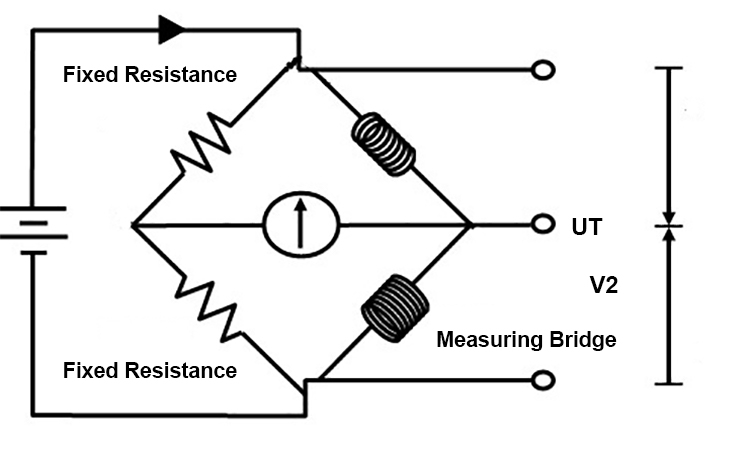
3. Catalytic Combustion Sensors
- Principle: Catalytic combustion sensors are used to detect combustible gases. They rely on the catalytic oxidation of the gas on a heated surface, leading to a change in temperature that is measured.
- Applications: Catalytic sensors are commonly used for detecting flammable gases such as Methane (CH4), Propane (C3H8), and Hydrogen (H2) in industrial and safety applications.
- Advantages: High sensitivity to combustible gases, rapid response times, and the ability to detect a wide range of flammable gases.
- Limitations: Require frequent maintenance, may be susceptible to poisoning by contaminants, and are not suitable for inert gases or non-combustible gases.
4. Infrared Sensors
- Principle: Infrared sensors operate based on the absorption of infrared light by gases at specific wavelengths. The amount of absorbed light is proportional to the gas concentration.
- Applications: Infrared sensors are effective for detecting gases like Methane (CH4), Carbon Dioxide (CO2), and hydrocarbons in industrial and environmental monitoring.
- Advantages: Excellent accuracy, stability, and resistance to interference from other gases. It can detect multiple gases simultaneously.
- Limitations: May be more expensive than some other sensor types. Not suitable for all gas types.
5. Photoionization Detectors (PIDs)
- Principle: PID sensors use high-energy ultraviolet (UV) light to ionize gas molecules, producing ions and electrons that can be detected as an electrical current.
- Applications: PID sensors are versatile and can detect a wide range of volatile organic compounds (VOCs) and other gases. They are used in environmental monitoring, industrial safety, and hazardous materials response.
- Advantages: Excellent sensitivity to VOCs and other gases, rapid response times, and can measure low concentrations.
- Limitations: These may require frequent calibration and are sensitive to contamination. Limited in distinguishing between different VOCs.
Each of these gas monitor sensor types has its specific strengths and limitations, making them suitable for different gas detection scenarios. The choice of sensor depends on factors such as the target gas, required sensitivity, response time, and environmental conditions. Calibration and regular maintenance are essential to ensure accurate and reliable gas detection results.
